In this fast-moving world, technology is advancing rapidly as Chinese scientists have built a mind-blowing nuclear battery. Never charging your phone and using it as much as you want is not a dream with this technology named BetaVolt. A ground-breaking Chinese company has claimed that it made a coin-sized “nuclear battery” that can produce power for up to 50 whole years without being charged. The technology has a radioactive isotope of nickel. To learn more about this technology, continue reading.
Size and dimensions:
The BetaVolt cell such as BV100 and is smaller in size than a coin. It measures 0.6 x 0.6 x 0.2 inches which will be 15 x 15 x 5 millimeters. The technology can efficiently generate 100 microwatts of power. If it gets approved for use in devices like smartphones, the next generation will never have to charge their phone as said by the company representatives of the cell.
How do the Nuclear Batteries work?
· Traditional batteries:
We are familiar with the fact that all batteries have common tasks to produce some amount of electric current for various tasks. Hence, in the case of traditional batteries, they rely on chemical reactions to generate current. But, eventually, a moment comes when the chemical reactions exhaust themselves leading to the battery’s demise.
· Nuclear battery:
Unlike traditional batteries, they use a radioactive material for their power source. As the radioisotope thermoelectric generator works in Voyager 1 space launched in 1977. And surprisingly, the RTG is still operational over 15 billion miles away from Earth. See how impressive is its longevity.
· Betavoltaic Generation
The innovation of BetaVolt depends on the generation of beta voltaic. Betavoltaic is a technology that captures the ejected electrons such as beta particles by the radioactive isotope of Nickel. It basically converts the ejected electrons into a usable electric current. In the betavolt battery, the radioactive nickel is sandwiched between the two ultra-thin plates of diamond.
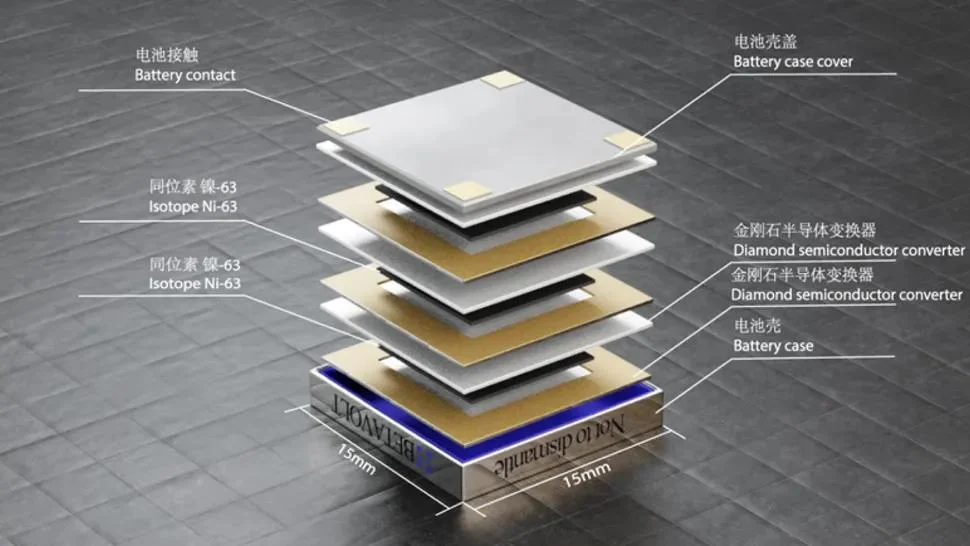
· Radioactive Decay
Nickel-63, an isotope of Nickel does an astonishing transformation inside the nuclear batteries. Due to the surplus neutrons, it becomes unstable which starts the decaying process. The neutron then decays into a proton that as a result releases a high-speed electron creating energy.
The nickel-63 decays into the copper by a beta pathway. Juan Claudio Nino, a materials scientist at the University of Florida explained “In simple terms, you have a neutron (a neutral subatomic particle) that transforms into a proton (a positive subatomic particle) by emitting an electron. If you can do something with that electron, it’s a source of electricity,”
· Shielding with materials:
The radioisotopes need special shielding with materials that can absorb harmful radiation if used in a cardiac pacing device or even a smartphone. The radioisotopes are dangerous to be used in space. Proper shielding is vital, as Juan Claudio Nino said; “The shielding here is critical because you don’t want something radioactive damaging the body,”.
The semi-conductor layer captures the electrons and conducts the electrons through the battery. Nino said; “A semiconductor is in-between a conductor like a metal and an insulator like rubber. The electrons can only move if they have enough energy so we can control them as they are moved,”.
Generally, lead or tungsten is mainly used as radiation protection but it is highly suggested to match the type and amount of shielding with the radioactive material used. To get more power, you simply use more concentration of radioactive source but then you will be required an extra amount of protection for that.
Can Betavolt last for half a century?
We all know that they have claimed that this nuclear battery can last for 50 years. But, let’s dive to learn more facts. The battery is a 3-volt cell that will have a power output of 100 microwatts that will produce a minuscule electric current of 0.000033A. Hence, the current that we will be getting through the decay of nickel atoms will consume 34.3 grams of nickel-63 for over 50 years. The used nickel-63 will be roughly the size of a sugar cube, isn’t it amazing?
Real-World Applications :
Nuclear batteries offer unparalleled longevity but are still impractical for smartphones as they have high power requirements. However, nuclear batteries will eventually find a niche in applications that can work on low and steady power requirements as remote sensors.



